IoT Trends Reshaping Smart Cities
Introduction to Smart Cities and IoT
Smart cities represent a progressive approach to urban development, characterized by the integration of technology and digital systems to enhance the quality of life for residents. At the core of this concept lies the Internet of Things (IoT), which encompasses a vast network of interconnected devices that collect, exchange, and analyze data. These data streams provide critical insights that enable city planners and administrators to optimize resources, improving infrastructure while simultaneously fostering a more sustainable urban environment.
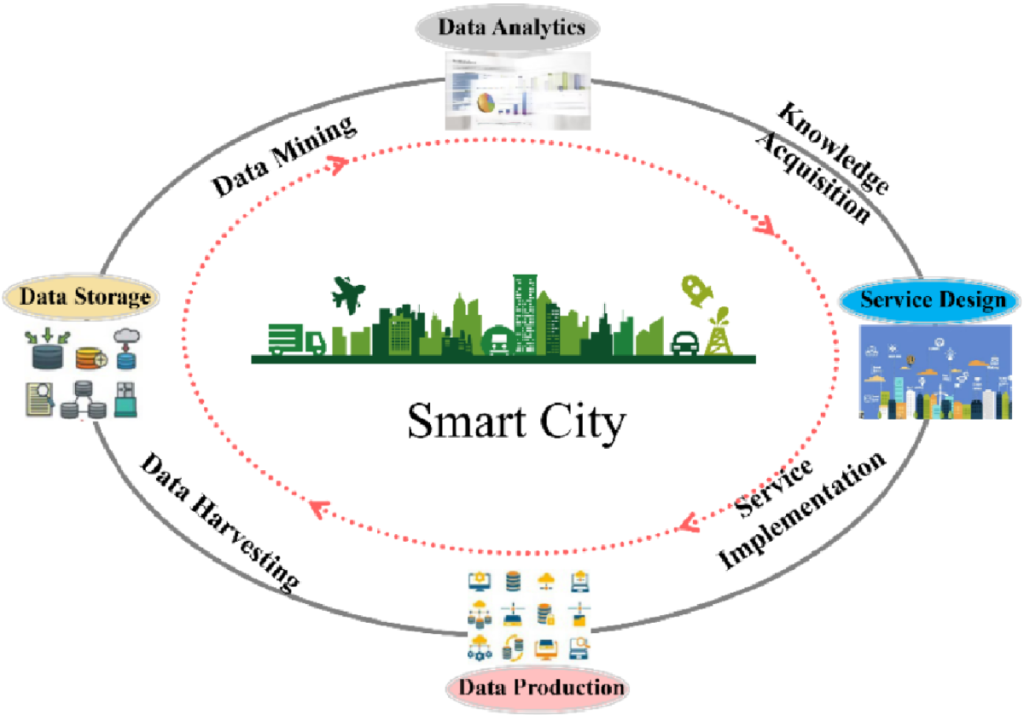
The foundational principles of smart cities revolve around creating efficient urban ecosystems that leverage technology to address various challenges. The implementation of IoT in this context plays a pivotal role by enabling real-time monitoring of city operations ranging from traffic management to waste disposal. For instance, smart traffic lights can adjust their timings based on live data, reducing congestion and improving traffic flow. Similarly, smart waste management systems utilize sensors to monitor waste levels in bins, leading to optimized collection routes and schedules that save both time and fuel.
Moreover, the benefits of adopting IoT technologies extend beyond operational efficiency; they significantly enhance sustainability initiatives. With access to precise data, cities can make informed decisions regarding energy consumption and resource allocation, thereby minimizing their carbon footprint. IoT applications facilitate smarter energy grids that balance supply and demand dynamically, ultimately leading to reduced utility costs for residents while promoting the use of renewable energy sources.
Enhancing the quality of life through smart cities also includes improved public safety and health services. IoT-enabled devices can provide timely alerts about environmental hazards, while connected health monitoring solutions ensure that healthcare providers deliver more efficient and personalized care to citizens. Thus, the convergence of IoT technology with urban infrastructure signifies a transformative movement toward smarter, more resilient city environments.
Key IoT Trends Impacting Smart Cities
The Internet of Things (IoT) is profoundly transforming the landscape of urban living, with several key trends driving the evolution of smart cities. One of the most significant advancements is in sensor technology. Modern cities are increasingly equipped with a variety of sensors that can monitor everything from traffic patterns to environmental conditions. These sensors collect real-time data, which can be utilized to optimize city services and enhance the quality of life for residents. For example, cities like Barcelona have implemented sensor-driven smart waste management systems that alert collection services when bins are full, thus streamlining operations and reducing costs.
Another pivotal trend reshaping smart cities is the roll-out of 5G connectivity. This next-generation network technology allows for faster data transmission and the simultaneous connection of multiple devices, which is essential for the seamless functioning of smart city applications. The increased bandwidth of 5G enables cities to deploy technologies such as autonomous vehicles and real-time public safety monitoring. For instance, cities such as San Francisco have started leveraging 5G networks to enhance their transportation systems, providing residents with real-time updates on public transport and traffic conditions.
Additionally, the utilization of big data and analytics has become paramount in urban planning and infrastructure management. By analyzing large datasets collected from various sources, city planners can make enlightened decisions that promote sustainable growth and enhance urban resilience. Cities like Singapore are at the forefront of this trend, as they utilize big data analytics to monitor and manage urban challenges such as congestion and energy use, facilitating a more responsive urban ecosystem.
In conclusion, the integration of advanced sensor technologies, the advent of 5G connectivity, and the strategic use of big data are key trends that are significantly impacting the development of smart cities. These trends not only enhance operational efficiency but also foster a more interconnected and sustainable urban living experience.
Challenges and Considerations in Implementing IoT in Smart Cities
The integration of Internet of Things (IoT) technologies into urban infrastructure presents numerous challenges that cities must navigate to ensure the efficacy and safety of smart city initiatives. One of the foremost concerns is data privacy. As smart cities increasingly rely on data collection from countless sensors and devices, the potential for personal information to be mishandled, or accessed by unauthorized parties, becomes increasingly significant. Municipalities must establish robust data governance frameworks to protect residents’ privacy while still leveraging data for city improvements.
Similarly, cybersecurity risks pose another substantial obstacle. With the interconnectivity of IoT devices, vulnerabilities in one area can have cascading effects throughout a city’s digital infrastructure. Cyberattacks targeting critical systems—such as traffic management, power grids, or public health infrastructure—could lead to disruptions and inefficiencies. Consequently, cities must invest in advanced cybersecurity measures, continuous monitoring, and regular updates for IoT systems to mitigate these risks effectively.
The issue of the digital divide cannot be overlooked either. In many urban settings, disparities in access to technology can create inequality, hindering the effectiveness of IoT applications intended to benefit all citizens. Ensuring equitable access to smart technologies requires targeted initiatives to bridge this gap, ensuring that all community members can partake in the advantages afforded by IoT solutions.
Moreover, the need for standardization across IoT devices and platforms remains a critical consideration. Without universally accepted standards, cities risk interoperability issues, which can complicate integration processes and inhibit the scalability of IoT frameworks. Stakeholder collaboration—including public sector entities, private organizations, and community residents—is crucial for establishing these standards and fostering public policy that supports sustainable smart city development.
Lastly, engaging the community is vital. Public awareness and involvement in smart city projects can lead to better adoption rates and user feedback, which are essential for shaping effective solutions. By addressing these multifaceted challenges, cities can harness the full potential of IoT technologies to create safer, more efficient, and resilient urban environments.
Future Outlook: The Next Steps for Smart Cities and IoT
As urban centers continue to evolve, the integration of the Internet of Things (IoT) technologies is poised to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of smart cities. The adaptation of cities to these innovative technologies will not only enhance operational efficiency but also improve the quality of life for residents. One significant trend anticipated in this evolution is the increased incorporation of artificial intelligence (AI) within IoT frameworks. AI algorithms can analyze large data sets generated by connected devices, enabling cities to make informed decisions regarding resource allocation, traffic management, and public safety.
Furthermore, the development of smart transportation systems will drastically enhance urban mobility. Future smart cities are expected to implement advanced IoT solutions such as connected public transportation networks, real-time traffic monitoring, and autonomous vehicles. These innovations aim to reduce congestion and provide seamless transit experiences to commuters, thus contributing to enhanced urban sustainability. As cities adopt these technologies, it becomes imperative that the integration is performed in a manner that addresses equity and accessibility concerns, ensuring that all citizens benefit from these advancements.
Sustainability remains a cornerstone of smart city development, with IoT technologies playing a crucial role in optimizing energy consumption and waste management. Cities are likely to invest in smart grids and intelligent waste disposal systems, driven by data analytics to minimize environmental footprints. Leaders must prioritize adaptive strategies to keep pace with the rapid acceleration of technology, fostering collaboration among stakeholders including government officials, private sectors, and local communities.
In conclusion, the future of smart cities hinges on the innovative deployment of IoT technologies, AI integration, and sustainable practices. As planners and leaders forge ahead, it will be essential to craft inclusive strategies that not only harness technological advancements but also promote social equity and environmental stewardship in urban environments.