The Transformative Benefits of Quantum Computing in Business
Understanding Quantum Computing
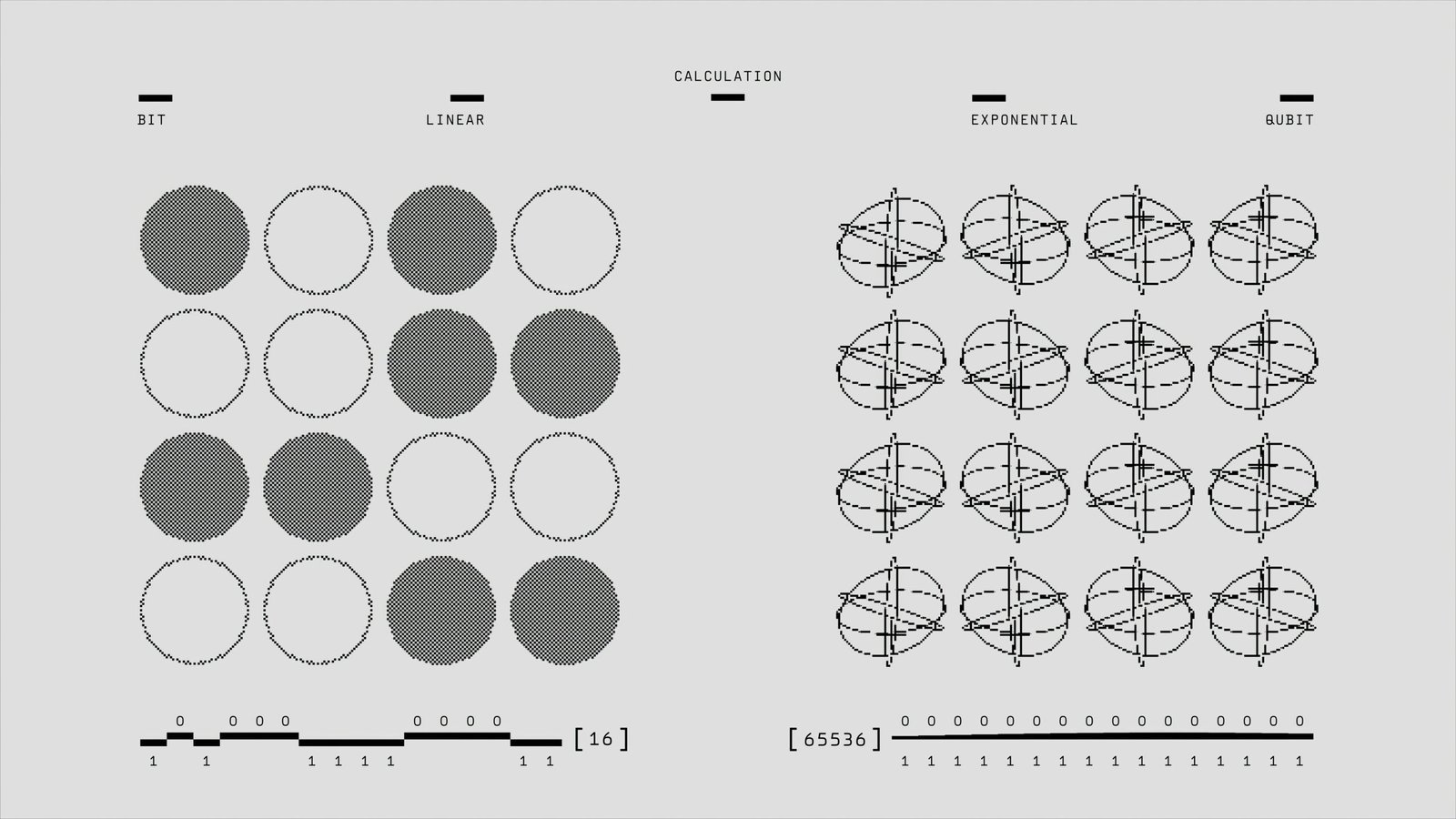
Quantum computing represents a fundamental shift from classical computing, leveraging the principles of quantum mechanics to process information in a radically different manner. In classical computing, the basic unit of information is the bit, which can hold a value of either 0 or 1. In contrast, quantum computing utilizes qubits, which have the unique ability to exist in multiple states simultaneously due to a phenomenon known as superposition. This characteristic allows quantum computers to perform complex calculations at unprecedented speeds and efficiencies.
Superposition enables qubits to represent both 0 and 1 at the same time, dramatically increasing the computational capacity available for processing data. With a system of just a few qubits, a quantum computer can perform many calculations simultaneously, offering a significant advantage over traditional systems. Moreover, when qubits are entangled, a property that describes the correlation between qubits regardless of the distance between them, quantum computing systems can achieve even greater computational power. This entanglement means that the state of one qubit can directly influence the state of another, leading to a new level of information processing capabilities.
The basic principles underlying quantum computing stem from quantum mechanics, which describes how particles behave at unimaginably small scales. Concepts such as uncertainty and wave-particle duality play crucial roles in the operation of quantum systems. As businesses recognize the transformative potential of quantum computing, a foundational understanding of these principles will be paramount. Grasping how qubits work, alongside the roles of superposition and entanglement, allows companies to envision the range of applications that quantum computing can unlock, from optimization problems to complex simulations that were once thought impractical.
Enhanced Problem-Solving Capabilities
Quantum computing is revolutionizing the way businesses approach complex problem-solving. Unlike classical computers, which operate using binary bits, quantum computers leverage qubits that can exist in multiple states simultaneously. This unique characteristic allows quantum systems to explore vast solution spaces much more efficiently, making them particularly adept at tackling problems that were previously considered intractable.
One significant application of quantum computing is in optimizing logistics and supply chain management. For instance, companies face challenges in determining the most efficient routes for delivery trucks to minimize fuel consumption and reduce operational costs. Traditional algorithms often struggle with the combinatorial explosion of possibilities as the number of delivery points increases. However, quantum algorithms can process these optimization challenges exponentially faster, yielding efficient routes that enhance productivity while decreasing expenses.
Similarly, in the realm of finance, quantum computing is making waves in financial modeling. For portfolio optimization, for example, firms can use quantum algorithms to analyze and simulate numerous market scenarios, allowing them to make data-driven decisions that optimize their returns while managing risk more effectively. A notable example can be observed in a project by a leading financial institution that implemented quantum models to predict pricing trends, resulting in significantly better predictive accuracy compared to classical methods.
In healthcare, the potential of quantum computing shines in drug discovery. The complexity of molecular interactions presents a significant challenge for classical computation. Quantum algorithms can simulate these interactions at unprecedented speeds, enabling researchers to identify promising drug candidates faster than ever before. Noteworthy advancements in this area have contributed to accelerated timelines for developing new treatments, therefore enhancing outcomes for patients.
These case studies illustrate that the enhanced problem-solving capabilities afforded by quantum computing not only streamline operations but also provide a competitive edge across industries. Embracing this technology could lead to substantial cost savings and innovative breakthroughs, highlighting its transformative potential in modern business practices.
Improved Data Security and Cryptography
The emergence of quantum computing presents a significant shift in the landscape of data security and cryptography. Quantum computers leverage the principles of quantum mechanics to process information in fundamentally different ways than classical computers. This capability allows for advanced techniques such as quantum key distribution (QKD), which promises to enhance data protection for businesses. QKD enables the secure exchange of cryptographic keys through quantum states, ensuring that any interception attempt will be immediately detectable. This feature could revolutionize encryption methods, offering robust solutions for sensitive data transmission.
Moreover, quantum encryption techniques utilize the unique properties of quantum bits (qubits) to create encryption keys that are inherently more secure than their classical counterparts. In this context, businesses can rest assured that their data is protected against unauthorized access, significantly reducing the risk of data breaches. As organizations increasingly depend on digital infrastructure for their operations, the importance of adopting these advanced security measures becomes paramount.
However, the rise of quantum computing is not without its challenges. While it brings considerable advancements in data protection, it also poses a threat to traditional cryptographic methods such as RSA and ECC. These classical encryption algorithms, which have relied on the complexity of mathematical problems for their security, may be vulnerable to quantum attacks. Quantum computers could efficiently factor large numbers or solve discrete logarithm problems, undermining the very foundations of existing encryption techniques. As a result, businesses must proactively adapt their security strategies to address these potential vulnerabilities and incorporate quantum-resistant algorithms into their systems.
Ultimately, while quantum computing heralds a new era of data security and cryptography, it compels businesses to reevaluate their dependency on traditional encryption methods and remain vigilant in the face of emerging threats.
Future Outlook and Strategic Adoption
The future of quantum computing in business is teeming with potential, as organizations increasingly recognize the technology’s transformative capabilities. Currently, the landscape of quantum technology is characterized by rapid advancements and heightened interest from key players in various industries. Major tech corporations, startups, and research institutions are all investing heavily in quantum computing, pushing the boundaries of this innovative frontier. This collaborative spirit is crucial, as it facilitates knowledge sharing and accelerates breakthroughs that can be integrated into commercial applications.
When assessing the timeline for mainstream adoption of quantum computing, experts indicate that while we are in the early stages, some practical applications may begin to emerge within the next five to ten years. For instance, sectors such as finance, pharmaceuticals, and logistics are poised to benefit significantly from quantum algorithms that enhance optimization, simulations, and machine learning. However, predicting the exact pace of adoption is challenging, given the complexity of the technology and the evolving regulatory environments that accompany it.
Despite its promising potential, businesses face several challenges in integrating quantum computing into their operations. These obstacles include limited access to hardware, a shortage of skilled professionals with expertise in quantum algorithms, and the necessity for substantial financial investment to develop quantum-ready infrastructures. Moreover, organizations need to rethink their data management strategies and integrate quantum literacy at all levels of their workforce. Addressing these challenges will be crucial for successful adoption.
To prepare for this transition, business leaders should consider establishing partnerships with quantum computing firms, academic institutions, and research organizations. Investments in training and development of quantum-specialized talent will also be vital. Furthermore, focusing on pilot projects that leverage quantum computing can help demystify the technology and identify valuable opportunities for organizational growth. Embracing a proactive approach will enable businesses to stay ahead in the evolving quantum landscape.